Stocks
Stock Basics
Stock Quotes
Common Stock
- A share of ownership in the corporation
- Confers rights to vote on election of directors, mergers, or other major events
-
Shareholder Voting
- Straight Voting
- Voting for directors during which shareholders must vote for each director separately
- Each shareholder having as many votes as shares held
- Cumulative Voting
- Voting for directors during which each shareholder is allocated votes equal to the number of open spots multiplied by his or her number of shares
- Classes of Stock
- Straight Voting
-
Shareholder Rights
- Annual Meeting
- Meeting held once per year at which shareholders vote on directors and other proposals
- As well as ask managers questions
- Proxy
- A written authorization for someone else to vote your shares
- Proxy Contest
- A contest between two or more groups competing to collect proxies to prevail in the matter up for shareholder vote
- Annual Meeting
Preferred Stock
- Stock with preference over common shares in payment of dividends and in liquidation
-
Cumulative Preferred Stock
- Preferred stock for which all missed preferred dividends must be paid before any common dividends may be paid
-
Non-Cumulative Preferred Stock
- Preferred stock for which missed preferred dividends do not accumulate.
- Only the current dividend is owed before common dividends may be paid
Ticker Symbol
- A unique abbreviation assigned to each publicly traded company
The Dividend-Discount Model
Two potential sources of cash flows from owning a stock:
- Dividends
- Selling Shares
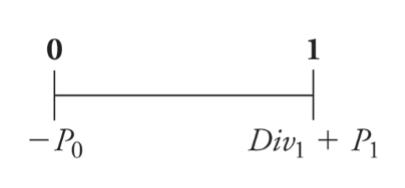
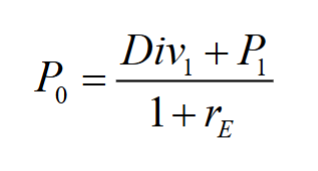
Dividend Yield
The expected annual divided of a stock divided by its current price
- the percentage return an investor expects to earn from the dividend paid by the stock
Capital Gain
The amount by which the selling price of an asset exceeds its initial purchase price
Capital Gains Rate
- An expression of capital gain as a percentage of the initial price of the asset
Total Return
The sum of a stock’s dividend yield and its capital gain rate
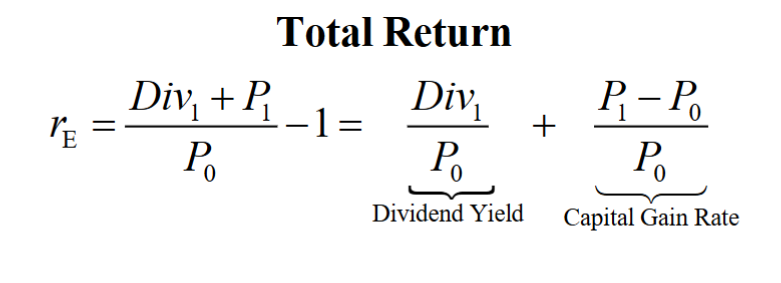
- The expected total return of the stock should equal the expected return of other investments available in the market with equivalent risk
Multi-Year Investor
If we hold the stock for more years, we would get multiple dividend payments
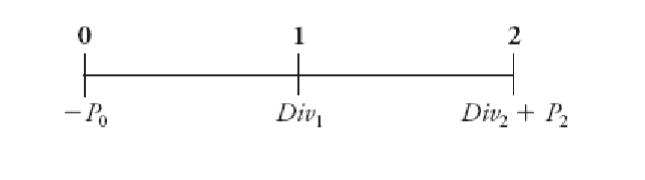
- As a two-year investor, we care about the dividend and stock price in year 2
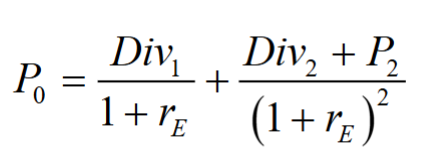
The price of the stock is equal to the present value of all of the expected future dividends it will pay, along with the cash flow from the sale in year N
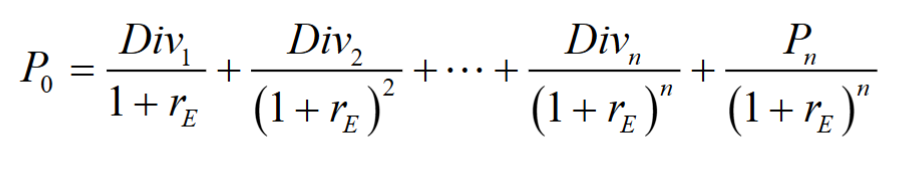
The price of a stock is equal to the present value of all of the expected future dividends it will pay
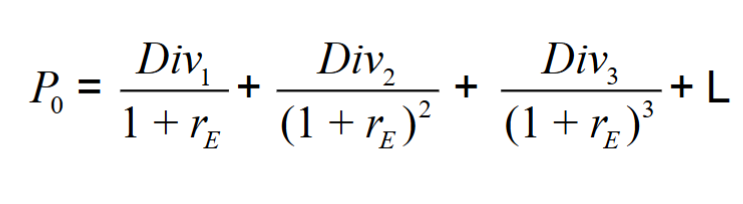
Estimating Dividends in the Dividend-Discount Model
Constant Dividend Growth Model
A model for valuing a stock by viewing its dividends as a constant growth perpetuity
- Assumes that dividends will grow at a constant rate,
, forever - The value of the firm depends on the dividend level of next year, divided by the equity cost of capital adjusted by the growth rate
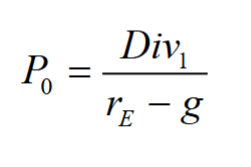
Dividends Versus Investment and Growth
A simple model of growth
- The dividend each year is equal to the firm’s earnings per share (EPS) multiplied by its dividend payout rate
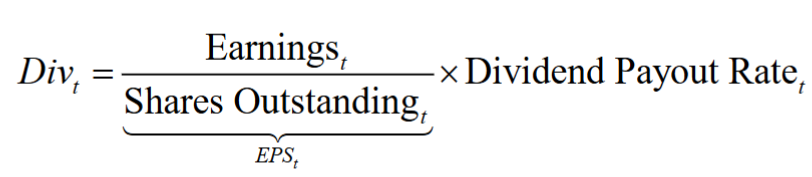
- The firm can increase its dividend in three ways:
- It can increase its earnings
- It can increase its dividend payout rate
- It can decrease its number of shares outstanding
- If all increases in future earnings result exclusively from new investment made with retained earnings, then:
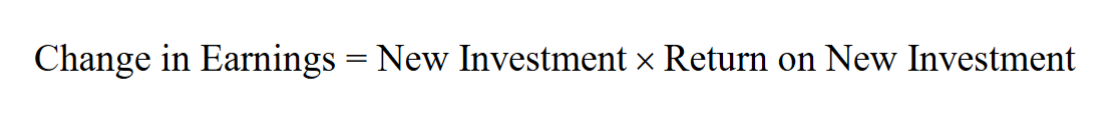
- New investment equals the firm’s earnings multiplied by its retention rate
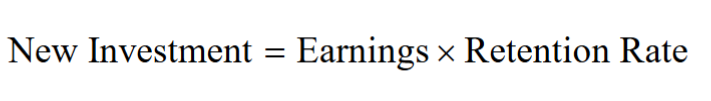
- The growth rate of earnings:
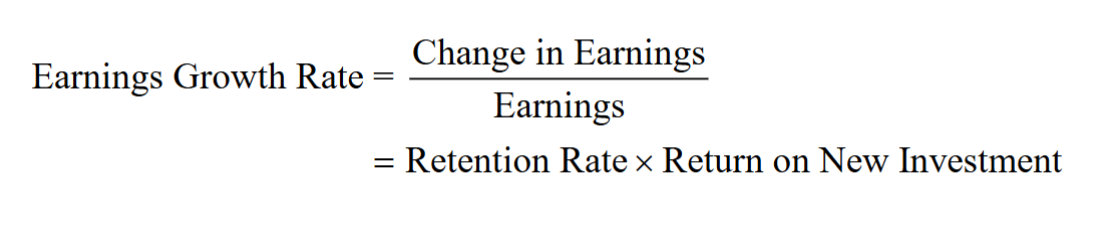
- If a firm chooses to keep its dividend payout rate constant, then the growth in its dividends will equal the growth in its earnings
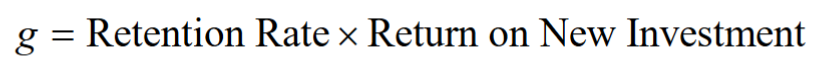
Changing Growth Rates
If the firm is expected to grow at a long-term rate
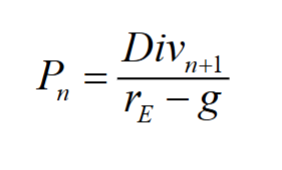
The dividend-discount model includes an implicit forecast of the firm’s profitability which is discounted back at the firm’s equity cost of capital
Limitations of the Dividend-Discount Model
Uncertain Dividend Forecasts
The dividend-discount model values a stock based on a forecast of the future dividends
- But a firm’s future dividends carry a tremendous amount of uncertainty
Non-Dividend Paying Stocks
Many companies do noy pay a dividends
- The dividend-discount model must be modified
Share Repurchases and the Total Payout Model
Share Repurchases
- The firm uses excess cash to buy back its own stock
Consequences - The more cash the firm uses to repurchase shares, the less cash it has available to pay dividends
- By repurchasing shares, the firm decreases its share count, which increases its earnings and dividends on a per-share basis
Total Payout Model
Values all of the firm’s equity, rather than a single share
- Discount the total payouts that the firm makes to shareholders
- Total amount spent on both dividends and share repurchases
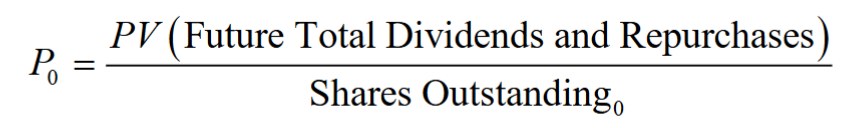
- Total amount spent on both dividends and share repurchases
The Discounted Free Cash Flow Model
This model determines the total value of the firm’s productive assets to all of its investors
- Both equity holders and debt holders
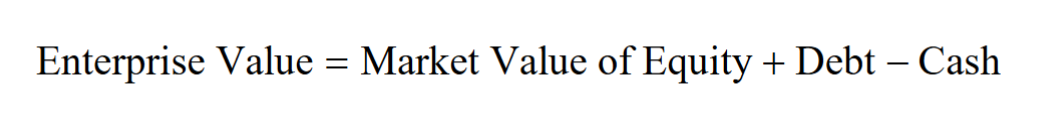
Valuing the Enterprise
- To estimate a firm’s enterprise value, we compute the present value of the firm’s free cash flow available to pay all investors
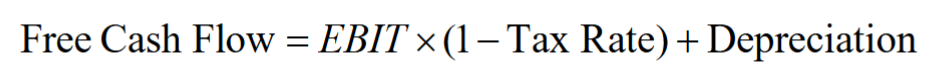
- Capital Expenditures - Increases in Net Working Capital
Discounted Free Cash Flow Model

Given the enterprise value, to solve for the value of equity and divide by the total number of shares outstanding
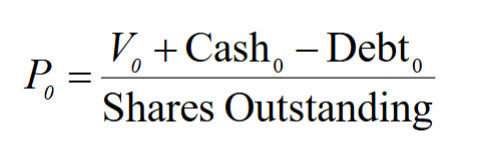
Implementing the Model
- Since we are discounting the cash flows to all investors, we use the weighted average cost of capital (WACC), denoted by
- The cost of capital that reflects the risk of the overall business, which is the combined risk of the firm’s equity and debt
- Forecast free cash flow up to some horizon, together with a terminal value of the enterprise
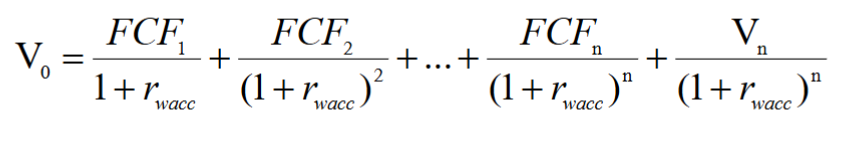
- Estimate the terminal value by assuming a constant long-run growth rate
for free cash flows beyond year - The long-run growth rate
is typically based on expected long-run growth rate of revenues
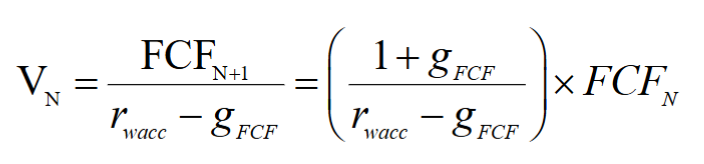
- The long-run growth rate
Connection to Capital Budgeting
- The firm’s future free cash flow in any particular year is equal to the sum of that year’s free cash flows from the firm’s current and future investment projects
- Firm’s enterprise value = The total value that the firm will generate from continuing its existing projects and initiating new ones
- NPV of any new project = its contribution to the firm’s enterprise value
- To maximize the firm’s share price, we should accept those projects that have a positive NPV
Limitations
We are making a lot of assumptions about future projections, e.g. constant growth, EBIT, which can result in large differences with small changes
Valuation Based on Comparable Firms
Method of Comparables
An estimate of the value of a firm based on the value of other, comparable firms or other investments that are expected to generate very similar cash flows in the future
- The Valuation Principle implies that two securities with identical cash flows must have the same price
- If these firms will generate identical cash flows, we can use the market value of the existing company to determine the value of the new firm
- We can adjust for scale differences using valuation multiples
Valuation Multiples
A ratio of a firm’s value to some measure of the firm’s scale or cash flow
- P/E ratio
- Enterprise Value Multiples
- Other multiples
- Multiples of sales
- assuming margins are similar in the future
- Price-to-book value of equity
- substantial tangible assets
- Industry-specific ratios
- Multiples of sales
Price-Earnings Ratio
- Most common valuation multiple
- Usually included in basic statistics computed for a stock
- Share price divided by earnings per share
We can compute a firm’s P/E ratio using: - Trailing Earnings: A firm’s earnings over the prior 12 months
- Forward Earnings: A firm’s anticipated earnings over the coming 12 months
The resulting ratio is: - Trailing P/E: A firm’s P/E ratio calculated using its trailing earnings
- Forward P/E: A firm’s P/E ratio calculated using its forward earnings
For valuation purposes, the forward P/E is generally preferred, as we are most concerned about future earnings
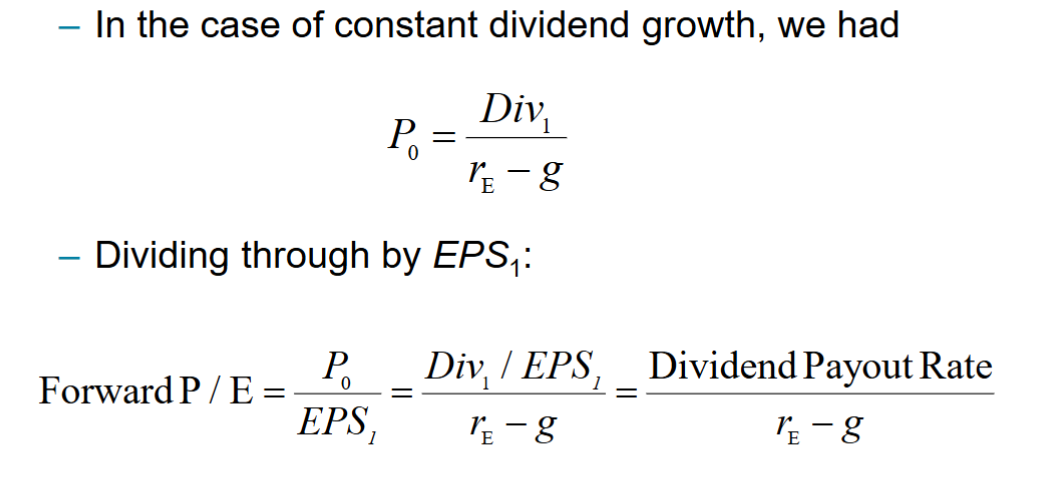
Enterprise Value Multiples
P/E ratio relates exclusively to equity, ignoring the effect of debt
Enterprise value multiples use a measure of earnings before interest payments are made
- EBIT
- EBITDA
- Free cash flow
- Because capital expenditure can vary between years, most common is to use enterprise value to EBITDA multiples
When we expect free cash flow growth is constant, we can writeto as:

- Because capital expenditure can vary between years, most common is to use enterprise value to EBITDA multiples
Limitations of Multiples
Firms are not identical
- Usefulness of a valuation multiple will depend on the nature of the differences and the sensitivity of the multiples to the difference
- Differences in multiple can be related to differences in
- Expected future growth
- Risk
- Differences in accounting conventions between countries
- Comparables provided only information regarding the value of the firm relative to other firms in the comparison set
- Cannot help determine whether an entire industry is overvalued
Comparison with Discounted Cash Flow Models
Valuation does not take into account material differences between firms
- Cannot help determine whether an entire industry is overvalued
- Talented managers
- More efficient manufacturing processes
- Patents on new technology
Discounted cash flow methods allow us to incorporate specific information about cost of capital or future growth - Potential to be more accurate
Information, Competition, and Stock Prices
Information in Stock Prices
- For a publicly traded firm, market price should already provide very accurate information regarding the true value of its shares
- A valuation model is best applied to tell us something about future cash flows or cost of capital, based on current stock price
- Only in relatively rare case in which we have some superior information that other investors lack would it make sense to second-guess the stock price
Competition and Efficient Markets
Efficient markets hypothesis
Implies that securities will be fairly priced, based on their future cash flows, given all information that is available to investors
Public, Easily Available Information
- Information available to all investors includes information in news reports, financial statements, corporate press releases, or other public data sources
Private or Difficult-to-Interpret Information
Individual Biases and Trading
Excessive Trading and Overconfidence
- Trading is expensive because of commissions and the difference between the bid and ask
- Given the difficulty of finding over- and under-valued stocks, you might expect individual investors to trade conservatively
- A study of the trading behaviour of individual investors at a discount brokerage found individual investors trade very actively
- Average turnover almost 50% above overall rates
- A study of the trading behaviour of individual investors at a discount brokerage found individual investors trade very actively
Overconfidence Hypothesis
Tendency of individual investors to trade too much based on the mistaken belief that they can pick winners and losers better than investment professionals
- Implication is that investors who trade more will not earn higher returns
- Performance will actually be worse because of trading costs
Disposition Effect
Investors tend to hold on to stocks that have lost value and sell stocks that have risen in value
- Investors’ increased willingness to take on risk in the face of possible losses
- Reluctance to admit a mistake by taking the loss
From a tax perspective, this behaviour tendency is costly - Capital gains are taxed only when an asset is sold
- delaying the tax payment reduces its present value
- Capital losses are tax deductible
- investors should capture tax losses early
Investor Attention, Mood, and Experience
- Individual investors are not generally full-time traders
- They have limited time and attention
- More likely to buy stocks that have been in the news, advertised more, had very high trading volume, or recently had extreme returns
- Investor mood affects investment behaviour
- Annualized market returns at the location of the stock exchange is higher on sunny days than on cloudy days
- Investors appear to put too much weight on their own experience rather than considering historical evidence
- People who grow up and live during a time of high stock returns are more likely to invest in stocks