Features and Constraints
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
- A set of variables
- a domain for each variable
- A set of constraints or evaluation functions
- Two kinds of problems:
- Satisfiability Problems:
- Find an assignment that satisfies constraints (hard constraints)
- Optimization Problems:
- Find an assignment that optimises the evaluation function (soft constraints)
- Satisfiability Problems:
- A solution to a CSP is an assignment to the variables that satisfies all constraints
- A solution is a model of the constraints
CSPs as Graph Searching Problems
Two ways to represent CSPs as a graph searching:
- Complete Assignment:
- Nodes:
- assignment of value to all variables
- Neighbors:
- change one variable value
- Nodes:
- Partial assignment:
- Nodes:
- assignment to first
variables
- assignment to first
- Neighbors:
- assignment to
variable
But,
- assignment to
- Nodes:
- These search spaces can get extremely large (thousands of variables), so the branching factors can be big
- Path to goal is not important, only the goal is
- No predefined starting nodes
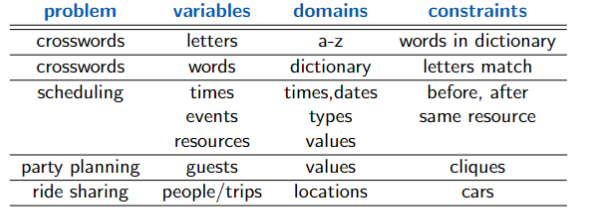
Classic CSP: Crossword Construction

Dual Representations
Two ways to represent the crossword as a CSP
- Primal representation
- Nodes represent word positions: 1-down, …, 6-across
- Domains are the words
- Constraints specify that the letters on the intersections must be the same
- Dual representation
- Nodes represent the individual squares
- Domains are the letters
- Constraints specify that the words must fit
Posing a CSP
Variables:
Domains: for each variable,
Constraints: Restrictions on the values a set of variables can jointly have
Constraints
- Can be N-ary, Over sets of
variables - e.g. “dual representation” for crossword puzzles with letters as domains
- word length
with constraint for each letter variables
- word length
- e.g. “dual representation” for crossword puzzles with letters as domains
- Here: Consider only Unary and Binary
- e.g. “first representation” for crossword puzzles with words as domains
- constraint on word length and intersection
- 1 or 2 variables
- e.g. “first representation” for crossword puzzles with words as domains
Solutions:
Generate and test
- Generate all possible assignments and test if it satisfies
Backtracking
- able to prune branches
- evaluate constraints as soon as they are grounded
- traverse in order
Consistency
- More general approach
- look for inconsistencies
- e.g. C=4 is inconsistent with any value of D since
- backtracking will “re-discover” this for every value of A, B
- e.g. C=4 is inconsistent with any value of D since
- graphical representation of constraints
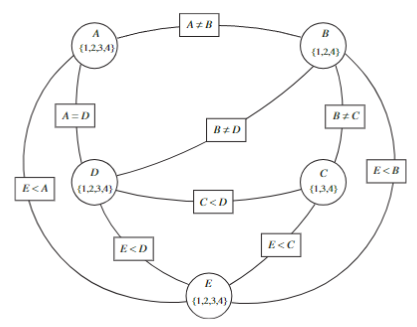
- Constraint Network (CN)
- domain constraint is unary constraint on values in a domain, written as
- A node in a CN is domain consistent if no domain value violates any domain constraint
- A CN is domain consistent if all nodes are domain consistent
- Arc
is a constraint on - An arc
is arc consistent if for each , there is some such that is satisfied - Bi-directional
- A CN is arc consistent if all arcs are arc consistent
- A set of variables
is path consistent if all arcs and domains are consistent
Formal Representation:
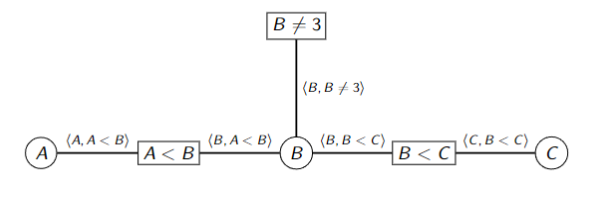
AC-3
Makes a CN arc consistent and domain consistent
- To-Do Arcs Queue (TDA) has all inconsistent arcs
- Make all domains domain consistent
- Put all arcs
in TDA - repeat
a. Select and remove an arcfrom TDA
b. Remove all values of domain ofthat don’t have a value in domain of that satisfies the constraint
c. If any were removed, Add all arcsto TDA
until TDA is empty
When AC-3 Terminates
AC-3 always terminates with one of these three conditions:
- Every domain is empty:
- there is no solution
- Every domain has a single value:
- has solution!
- Some domain has more than one value:
- split it in two, run AC-3 recursively on two halves
- don’t have to start from scratch
- only have to put back all arcs
if was the domain that was split
- only have to put back all arcs
- Connection between domain splitting and search
Complexity
variables, binary constraints, and the size of each domain is at most - Time complexity:
- Each arc
can be added to the queue at most times because we can delete at most values from
- Each arc
- Checking consistency of each arc can be done in
time
Variable Elimination
Idea: Eliminate the variables one-by-one passing their constraints to their neighbors
- When there is a single variable remaining, if it has no values, the network was inconsistent
- The variables are eliminated according to some elimination ordering
- Different elimination orderings result in different size intermediate constraints
- If there is only one variable, return the intersection of the (unary) constraints that contain it
- Select a variable
- Join the constraints in which
appears, forming constraint - Project
onto its variables other than : call this - Place new constraint
between all variables that were connected to - Remove
- Recursively solve the simplified problem
- Return
joined with the recursive solution
- Join the constraints in which
Hill-Climbing
Randomized incl. Local Search
Local Search
- Maintain an assignment of a value to each variable
- At each step, select a neighbor of the current assignment
- e.g. one that improves some heuristic value
- Stop when a satisfying assignment is found, or return the best assignment found
Requires:
- What is a neighbor?
- Which neighbor should be selected?
Local Search for CSPs
- Aim is to find an assignment with zero unsatisfied constraints
- Given an assignment of a value to each variable, a conflict is an unsatisfied constraint
- The goal is an assignment with zero conflicts
- Heuristic function to be minimized:
- the number of conflicts
Greedy Descent Variants
- Find the variable-pair that minimizes the number of conflicts at every step
- Select a variable that participates in the most number of conflicts. Select a value that minimizes the number of conflicts
- Select a variable that appears in any conflict. Select a value that minimizes the number of conflicts
- Select a variable at random. Select a value that minimizes the number of conflicts
- Select a variable and value at random; accept this change if it doesn’t increase the number of conflicts
Problems with Greedy Descent
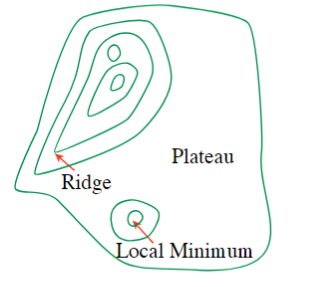
- A local minimum that is not a global minimum
- A plateau where the heuristic values are uninformative
- A ridge is a local minimum where
-step look ahead might help
Randomized Greedy Descent
As well as downward steps we can allow for:
- Random steps: move to a random neighbor
- Random restart: reassign random values to all variables
Which is more expensive computationally? - A mix of the two = stochastic local search
High Dimensional Search Spaces
- In high dimensions the search space is less easy to visualize
- Often consists of long, nearly flat ”canyons”
- Hard to optimize using local search
- Step-size can be adjusted
Stochastic Local Search
A mix of:
- Greedy descent:
- Move to a lowest neighbor
- Random walk:
- Taking some random steps
- Random restart:
- Reassigning values to all variables
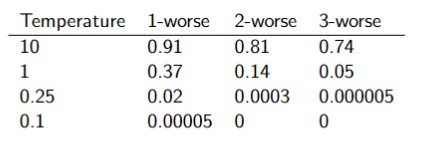
Variant: Simulated Annealing
- Pick a variable at random and a new value at random
- If it is an improvement, adopt it
- If it isn’t an improvement, adopt it probabilistically depending on a temperature parameter,
- With current assignment
and proposed assignment we move to with probability
- With current assignment
- Temperature can be reduced
Probability of accepting a change:

Tabu Lists
- recall GSAT:
- never choose same variable twice
- To prevent cycling we can maintain a tabu list of the
last assignments - Don’t allow an assignment that is already on the tabu list
- If
, we don’t allow an assignment of to the same value to the variable chosen - We can implement it more efficiently than as a list of complete assignments
- It can be expensive if
is large
Parallel Search
A total assignment is called an individual
- Maintain a population of
individuals instead of one - At every stage, update each individual in the population
- Whenever an individual is a solution, it can be reported
- Like
restarts, but uses times the minimum number of steps
Beam Search
- Like parallel search, with
individuals, but choose the best out of all of the neighbors - all if there are less than
- all if there are less than
- When
, it is greedy descent - The value of
lets us limit space and parallelism
Stochastic Beam Search
Like beam search, but it probabilistically chooses the
- The probability that a neighbor is chosen is proportional to its heuristic value:
- This maintains diversity amongst the individuals
- The heuristic value reflects the fitness of the individual
- Like asexual reproduction:
- each individual mutates and the fittest ones survive
Genetic Algorithms
Like stochastic beam search, but pairs of individuals are combined to create the offspring:
- For each generation:
- Randomly choose pairs of individuals where the fittest individuals are more likely to be chosen
- For each pair, perform a cross-over: form two offspring each taking different parts of their parents:
- Mutate some values
- Stop when a solution is found
Crossover
- Given two individuals:
- Select
at random - Form two offspring:
- The effectiveness depends on the ordering of the variables
- Many variations
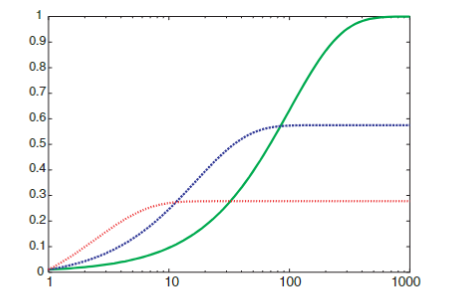
Compare Stochastic Algorithms
How can you compare three algorithms when
- One solves the problem 30% of the time very quickly but doesn’t halt for the other 70%
- One solves 60% of the cases reasonably quickly but doesn’t solve the rest
- One solves the problem in 100% of the cases, but slowly
Plots runtime and the proportion of the runs that are solved within that runtime