Decision Making
Planning Under Uncertainty
Bayesian Decision Making
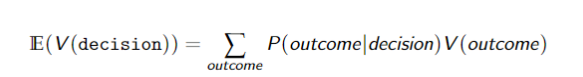
Can also add context so

Preferences
- Actions result in outcomes
- Agents have preferences over outcomes
- A (decision-theoretic) rational agent will do the action that has the best outcome for them
- Sometimes agents don’t know the outcomes of the actions, but they still need to compare actions
- Agents have to act
- doing nothing is often a meaningful action
Preferences Over Outcomes
If
means is at least as desirable as - weak preference
means and - indifference
means and - strong preference
Lotteries
An agent may not know the outcomes of their actions, but only have a probability distribution of the outcomes
- A lottery is a probability distribution over outcomes. It is written $$\left[p_1:o_1, p_2:o_2, \cdots, p_k:o_k\right]$$where the
are outcomes and such that$$\sum_ip_i = 1$$The lottery specifies: outcome occurs with probability
When we talk about outcomes, we will include lotteries
Properties of Preferences
Completeness
- Agents have to act, so they must have preferences
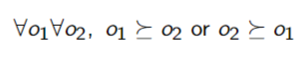
Transitivity - Preferences must be transitive
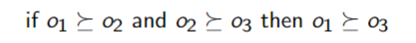
Monotonicity - An agent prefers a larger chance of getting a better outcome than a smaller chance
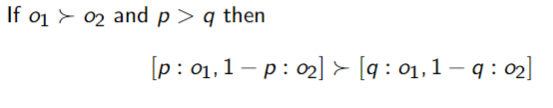
Continuity - Suppose
and , then there exists a such that
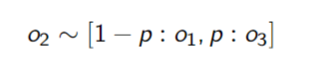
Decomposability - An agent is indifferent between lotteries that have same probabilities and outcomes
Substitutability - if
then the agent is indifferent between lotteries that only differ by and
Theorem
If preferences follow the preceding properties, then the preferences can be measured by a function
such that
if and only if - Utilities are linear with probabilities:
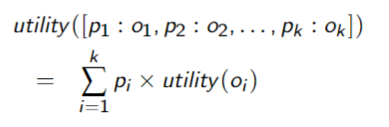
Rationality and Irrationality
Rational agents act so as to maximize expected utility:
- Action
leads to outcome with probabilities - Action
leads to outcome with probabilities - if
- then action
is the rational choice
- then action
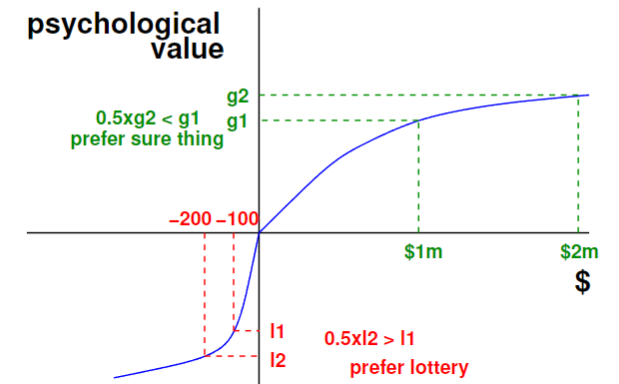
Prospect Theory - Tversky and Kahneman
Humans weight value differently for gains vs losses
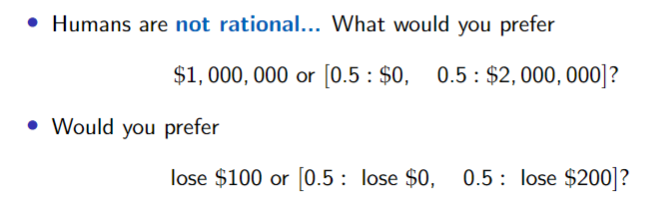
Ultimatum Game
- Two-player game: agents
and gets $10 can offer any amount can - accept:
gets , gets - reject:
and both get 0
- accept:
- rational choice:
offers , accepts - Humans:
Making Decisions Under Uncertainty
What an agent should do depends on:
- The agent’s ability
- what options are available to it
- The agent’s beliefs
- the ways the world could be, given the agent’s knowledge
- Sensing the world updates the agent’s beliefs
- The agent’s preferences
- what the agent actually wants and the tradeoffs when there are risks
Decision theory specifies how to trade off the desirability and probabilities of the possible outcomes for competing actions
- what the agent actually wants and the tradeoffs when there are risks
Single Decisions
Decision variables are like random variables that an agent gets to choose the value of
- Ina single decision variable, the agents can choose
for any
Expected utility of decisionleading to outcomes for utility function
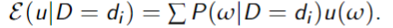
An optimal single decision is the decisionwhose expected utility is maximal:
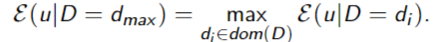
Decision Networks
A decision network is a graphical representation of a finite sequential decision problem
- Decision networks extend belief networks to include decision variables and utility
A decision network specifies what information is available when the agent has to act
A decision network specifies which variables the utility depends on
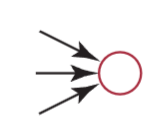
A random variable is drawn as a ellipse - Arcs into the node represent probabilistic dependence
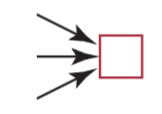
A decision variable is drawn as a rectangle - Arcs into the node represent information available when the decision is made

A utility node is drawn as a diamond - Arcs into the node represent variables that the utility depends on
Example
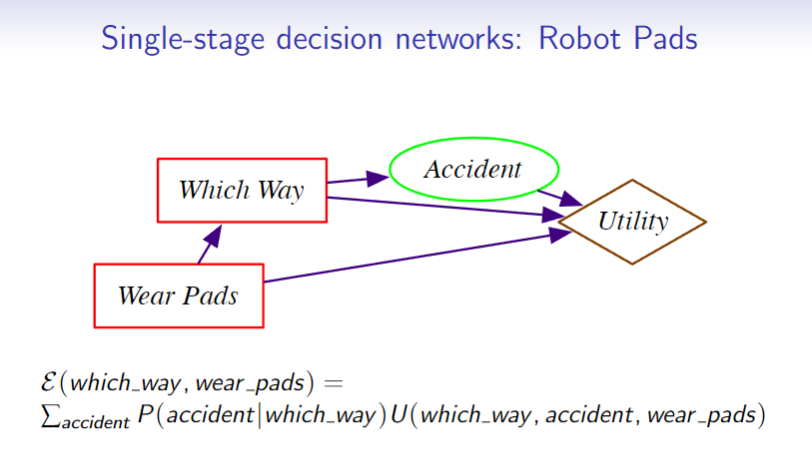
Finding the Optimal Decision
Suppose the random variables are
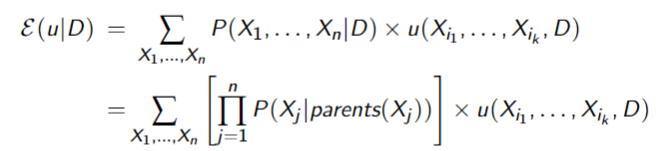
- where
may include
To find the optimal decision: - Create a factor for each conditional probability and for the utility
- Multiply together and sum out all of the random variables
- This creates a factor on
that gives the expected utility for each - Choose the
with the maximum value in the factor
Sequential Decisions
An intelligent agent doesn’t make a multi-step decision and carry it out without considering revising it based on future information
- A more typical scenario is where the agent:
- observes, acts, observes, acts
- Subsequent actions can depend on what is observed
- What is observed depends on previous actions
- Often the sole reason for carrying out an action is to provide information for future actions
- e.g. diagnostic tests, spying
Sequential decision problems
A sequential decision problem consists of a sequence of decision variables
- Each
has an information set of variables , whose value will be known at the time decision is made
Policies
A policy specifies what an agent should do under each circumstance
- A policy is a sequence
of decision functions$$\delta_i : dom(parents(D_i)) \rightarrow dom(D_i)$$
This policy means that when the agent has observed, it will do
Expected Utility of a Policy
The expected utility of policy

An optimal policy is one with the highest expect utility
Finding the Optimal Policy
- Create a factor for each conditional probability table and a factor for the utility
- Set remaining decision nodes ← all decision nodes
- Multiply factors and sum out variables that are not parents of a remaining decision node
- Select and remove a decision variable
from the list of remaining decision nodes: - pick one that is in a factor with only itself and some of its parents (no children)
- Eliminate
by maximizing. This returns: - the optimal decision function for
, - a new factor to use,
- the optimal decision function for
- Repeat 3-5 until there are no more remaining decision nodes
- Eliminate the remaining random variables
- Multiply the factors: this is the expected utility of the optimal policy
- If any nodes were in evidence, divide by the P(evidence)
Agents as Processes
Agent carry out actions:
- forever - infinite horizon
- until some stopping criteria is met - indefinite horizon
- finite and fixed number of steps - finite horizon
Decision-Theoretic Planning
What should an agent do when
- it gets rewards and punishments and tries to maximize its rewards received
- actions can be noisy;
- the outcome of an action can’t be fully predicted
- there is a model that specifies the probabilistic outcome of actions
- the world is fully observable:
- the current state is always full in evidence
World State
The world state is the information such that if you knew the world state, no information about the past is relevant to the future
- Markovian assumption
Letbe the state, action at time

is the probability that the agent will be in state immediately after doing action in state - The dynamics is stationary if the distribution is the same for each time point
Decision Processes

A Markov decision process augments a Markov chain with actions and values
Markov Decision Processes
For an MDP you specify:
- set
of states - set of
of actions specifies the dynamics specifies the reward. - The agents gets a reward at each time step (rather than just a final reward)
is the expected reward received when the agent is in state , does action and ends up in state
Information Availability
What information is available when the agent decides what to do?
- fully-observable MDP
- the agent gets to observe
when deciding on action
- the agent gets to observe
- partially-observable MDP (POMDP)
- the agent has some noisy sensor of the state
- it needs to remember its sensing and acting history
- it can do this by maintaining a sufficiently complex belief state
Rewards and Values
Suppose the agent receives the sequence of rewards
- Total reward
- Average reward
- Discounted reward
is the discount factor
Policies
A stationary policy is a function:
Given a state
- An optimal policy is one with maximum expected discounted reward
- For a fully-observable MDP with stationary dynamics and rewards with infinite or indefinite horizon, there is always an optimal stationary policy
Value of a Policy
, where is an action and is a state, is the expected value of doing in state , then following policy , where is a state, is the expected value of following policy in state and can be defined mutually recursively:
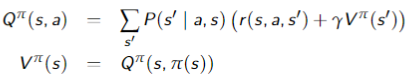
Value of the Optimal Policy
is the optimal action to take in state , where is an action and is a state, is the expected value of doing in state , then following the optimal policy , where is a state, is the expected value of following the optimal policy in state and can be defined mutually recursively:
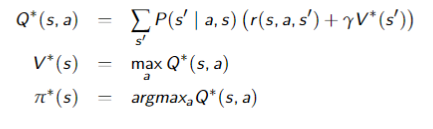
Value Iteration
The
- Idea: Given an estimate of the
-step lookahead value function, determine the -step lookahead value function
Algorithm
- Set
arbitrarily, - Compute
from $V^{t-1}
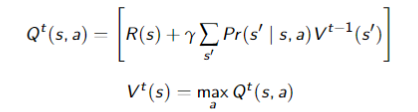
- The policy with
stages to go is simply the action that maximizes this 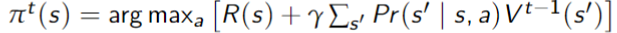
- This is dynamic programming
- This converges exponentially fast (in
) to the optimal value function - Convergence when
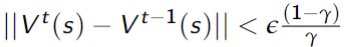
is within of optimal 
Asynchronous Value Iteration
You don’t need to sweep through all the states
- can update the value functions for each state individually
- This converges to the optimal value functions, if each state and action is visited infinitely often in the limit
- You can either store
or
Storing
Repeat forever:
- Select state
;
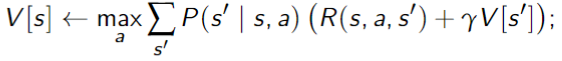
- select action
; - using an exploration policy
Storing
Repeat forever:
- Select state
, action ;
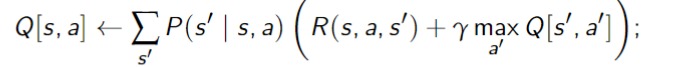
Markov Decision Processes: Factored State
Represent
- for each
and each action , we have - Reward
may be additive:
Value iteration proceeds as usual but can do one variable at a time
- e.g. variable elimination
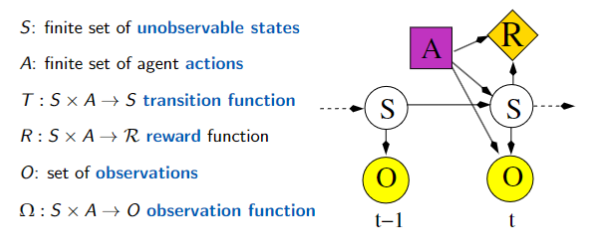
Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes (POMDPs)
A POMDP is like an MDP, but some variables are not observed
- It is a tuple
Value Functions and Conditional Plans

- Pieces are called
vectors

Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)

Reinforcement Learning
What should an agent do given:
- prior knowledge
- possible states of the world
- possible actions
- observations
- current state of world
- immediate reward / punishment
- goal
- act to maximize accumulated reward
Like decision-theoretic planning, except model of dynamics and model of reward not given
- act to maximize accumulated reward
- Need to balance between gathering information and acting optimally
Experiences
We assume there is a sequence of experiences:
What should the agent do next?- It must decide whether to:
- explore to gain more knowledge
- exploit the knowledge it has already discovered
Why is reinforcement learning hard?
Credit Assignment Problem: What actions are responsible for the reward may have occurred a long time before the reward was received
- The long-term effect of an action of the robot depends on what it will do in the future
- The explore-exploit dilemma:
- at each time should the robot be greedy or inquisitive
Main Approaches
See through a space of policies (controllers)
- Model Based RL: Learn a model consisting of state transition function
and reward function ; - Solve as an MDP
- Model-Free RL: Learn
, use this to guide action.
Temporal Differences
Suppose we have a sequence of values: $$v_1, v_2, v_3, \cdots$$ And want a running estimate of the average of the first
When a new value
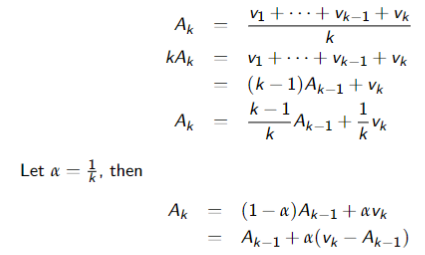
”TD formula”
- Often we use this update with
fixed
Q-Learning
Idea: store
- Update this as in asynchronous value iteration
- but using experience (empirical probabilities and rewards)
Suppose the agent has an experience - This provides one piece of data to update
- The experience
provides the data point:$$r + \gamma \max_{a'}Q[s',a']$$which can be used in the TD formula giving:
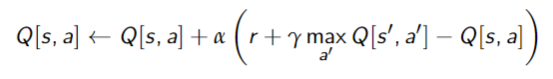
Pseudocode

Properties of Q-learning
Q-learning converges to the optimal policy, no matter what the agent does, as long as it tries each action in each state enough
- But what should the agent do?
- exploit: when in state
, select the action that maximizes - explore: select another action
- exploit: when in state
Exploration strategies:
The
- choose a random action with probability
and choose a best action with probability
Softmax action selection: - in state
choose action with probability

- where
is the temperature - good actions are chosen more often than bad actions
defines how good actions are chosen - For
, all actions are equiprobable - For
, only the best is chosen
Optimism in the face of uncertainty:
- initialize
to values that encourage exploration
Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) - also store
- number of times that state-action pair has been tried
- and use

Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Model-based reinforcement learning uses the experiences in a more effective manner
- it is used when collecting experiences is expensive
- e.g. in a robot or an online game
- and you can do lots of computation between each experience
- idea: learn the MDO and interleave acting and planning
- After each experience update probabilities and reward
- then do some steps of asynchronous value iteration
Model-based learner

Off/On-policy Learning
Q-learning does off-policy learning:
- it learns the value of the optimal policy, no matter what it does
- this could be bad if the exploration policy is dangerous
On-policy learning learns the value of the policy being followed - e.g. act greedily 80% of the time and act randomly 20% of the time
- If the agent is actually going to explore, it may be better to optimize the actual policy it is going to do
SARSA uses the experienceto update
SARSA

Q-function Approximations
Let
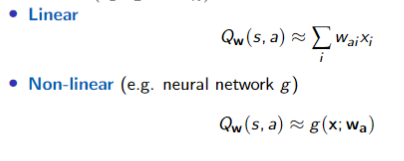
Approximating the Q-function
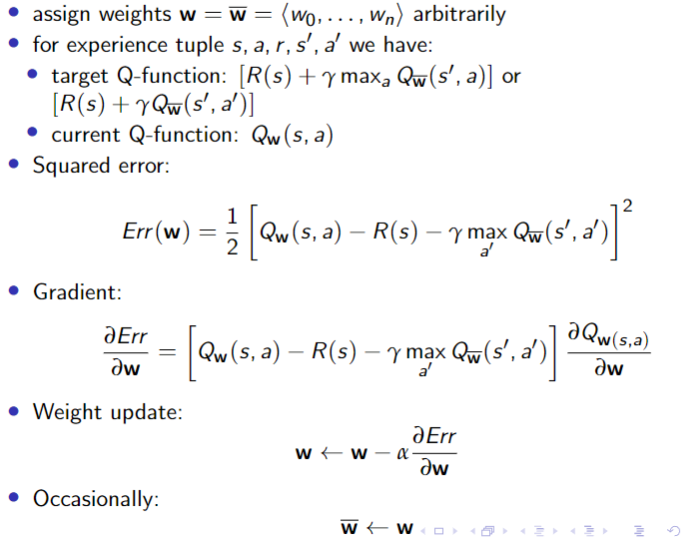
SARSA with linear function approximation

Convergence
Linear Q-learning
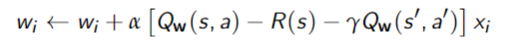
Non-linear Q-learning
- Adjusting
to increase at might introduce errors at nearby state-action pairs
Mitigating Divergence
Two tricks used in practice:
- Experience Replay
- Use two
function (two networks): network (currently being updated) - Target network (occasionally updated)
Experience Replay
Idea: Store previous experiences
- Breaks correlations between successive updates
- more stable learning
- Few interactions with environment needed to converge
- greater data efficiency
Target Network
Idea: use a separate target network that is updated only periodically
- target network has weights
and computes - repeat for each
in mini-batch:
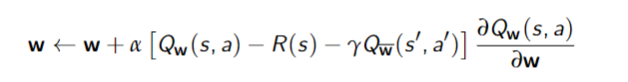
Deep Q-Network

Bayesian Reinforcement Learning
- Include the parameters in the state space
- transition function and observation function
- Model-based learning through inference
- belief state
- State space is now continuous
- belief space is a space of continuous functions
- Can mitigate complexity by modelling reachable beliefs
- optimal exploration-exploitation trade-off