Agents
Situated Agent
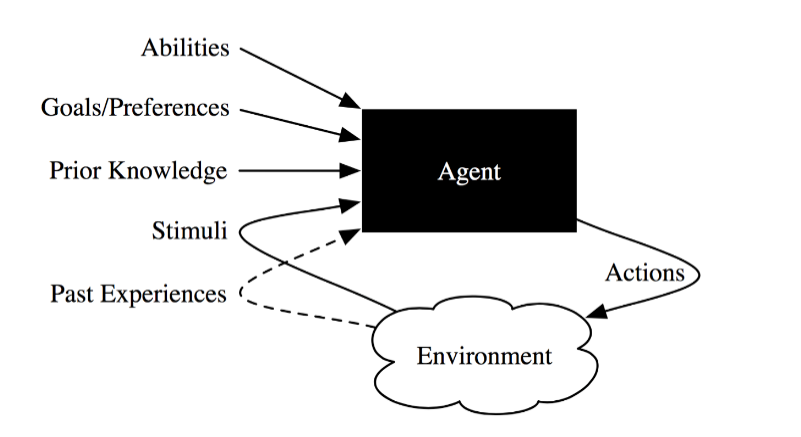
An agent is an entity that performs actions in its environment
- Agent + Environment = World
- Inside black box: belief state
Example:
Domain for Delivery Robot
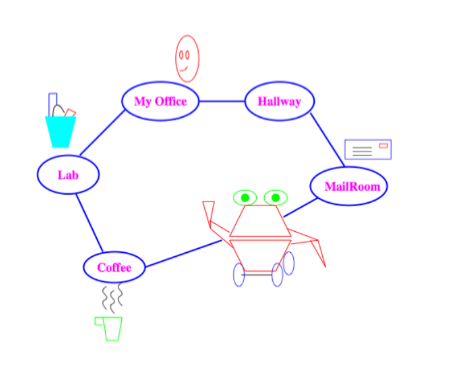
This robot must:
- Deliver coffee and mail when needed
- Avoid getting wet
Abilities: Movement, speech, pickup and place objects, sense weather
Stimuli: Information about its environment from cameras, sonar, sound, laser range finders, or keyboards
Prior knowledge: its capabilities, objects it may encounter, maps
Past experience: which actions are useful and when, what objects are there, how its actions affect its position
Goals: what it needs to deliver and when, trade offs between acting quickly and acting safely, effects of getting wet
What does the delivery robot need to do?
- Determine where the user is, where the coffee is, …
- Find a path between locations
- Plan how to carry out multiple tasks
- Make default assumptions about where user is
- Make trade offs under uncertainty:
- Should it go near stairs or outside?
- Learn from experience
- Sense and act in the world, avoid obstacles, pickup and put down coffee, deliver mail
Knowledge Representation
Knowledge: Information used to solve tasks
Representation: Data structures used to encode knowledge
Knowledge Base (KB): representation of all knowledge
Model: Relationship of KB to world
Level of Abstraction: How accurate is the model
Non-AI:
- Specify how to compute something
- Specify what the next step is
- Programmer figures out how to dot he computation
AI: - Specify what needs to be computed
- Specify how the world works
- Agent figures out h ow to do the ocmputation
Dimensions of Complexity
1. Modularity
flat → modular → hierarchical
2. Planning Horizon
Non-planning → finite horizon → indefinite horizon → infinite horizon
How far the agent looks into the future when deciding what to do
- Static: world does not change
- Finite horizon: agent reasons about a fixed finite number of time steps
- Indefinite horizon: agent is reasoning about finite, but not predetermined, number of time steps (e.g. until goal completion)
- Infinite horizon: the agent plans for going on forever
3. Representation
Explicit states → features → individuals and relations
An agent can reason in terms of:
- Explicit states: a state directly represents one way the world could be
- Features or propositions:
- Often more natural to describe states in terms of features
- 30 binary features can represent
states
- Individuals and relations:
- There is a feature for each relationship on each tuple of individuals
- Often we can reason without knowing the individuals or when there are infinitely many individuals
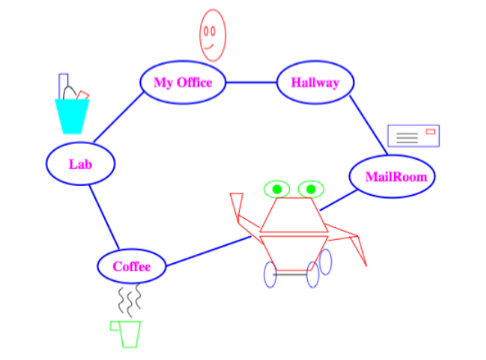
- Explicit: enumeration of all worlds,
- Features: robot location, user location, robot has coffee?,
- Relations: robot moves (clockwise + or counter-clockwise -)
4. Computational Limits
Perfect rationality → Bounded rationality
Do we have time to calculate exact solutions?
- Perfect rationality: Agent always chooses the optimal action
- Bounding rationality: Agent chooses a possibly sub-optimal action given its limited computational capacity
- Satisficing solution
- Approximately optimal solution
5. Learning
Knowledge is given → knowledge is learned
6. Uncertainty
Fully observable → partially observable
World dynamics: deterministic → stochastic
What the agent can determine the state from the observations:
- Fully-observable: the agent knows the state of the world from the observations
- Partially-observable: there can be many states that are possible given as observation
If the agent knew the initial state and the action, could it predict the resulting state? - Deterministic: the state resulting from carrying out an action in state is determined from the action and the state
- Stochastic: there is uncertainty over the states resulting from executing a given action in a given state
7. Preference
Goals → complex preferences
- Achievement goal is a goal to achieve
- can be a complex logical formula
- Maintenance goal is a goal to be maintained
- Complex preferences that may involve trade offs between various desiderata, perhaps at different times
- can be either ordinal or cardinal
8. Reasoning by number of agents
Single agent → adversarial → multiagent
- Single agent reasoning is where an agent assumes that any other agents are part of the environment (delivery robot)
- Adversarial reasoning considers another agent acts in opposition to our goals (AlphaGo)
- Multiagent reasoning is when an agent needs to reason strategically about the reasoning of other agents (robot soccer, trading agent)
Agents can have their own goals: cooperative, competitive, or goals can be independent of each other
9. Interactivity
Offline → online