Vision and Language
Why Vision + Language?
- We live in a multi-modal world
- We learn from both vision and language modalities
- Allows AI to interact with human beings
- Language provides open–set and comprehensive semantic information for visual perception

Vision-language Joint Embedding
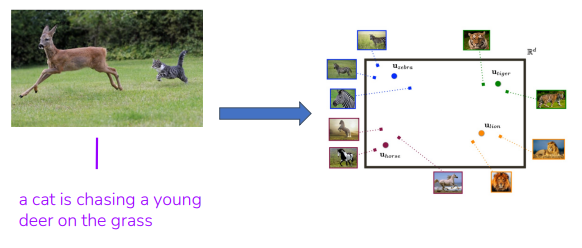
What is a vision-language joint embedding space?

Why vision-language joint embedding?
- Enrich training samples & labels for visual recognition model
- Samples: annotated images are considerably limited VS. image-text pairs
- Labels: Generalizing to unseen object categories
- Image-text / text-image retrieval
- Useful for downstream vision-language tasks
How is Vision-Language Joint Embedding Learned?
- Data: image-text pairs
- Joint embedding: Alignment!
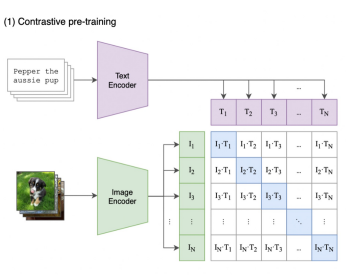
CLIP
Rather than needing handcrafted labels to train a good classifier for a given domain, we can leverage free-form text from the internet to learn a model that is a good classifier for all domains
Training
- CLIP is trained to classify which text caption in a batch corresponds to each image in a batch
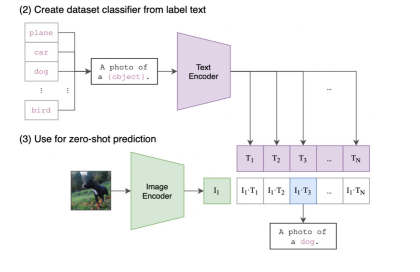
Inference
- Create new zero-shot classifiers during inference:
- fetch the text embeddings for a set of classification labels
- compute these labels’ similarity to a given image
Evaluation and Applications
- Calculate image-text similarities
- Image-text retrieval based on image-text similarities
- Image classification
- Representation learning
ImageBind
Bridging More Modalities
- One embedding space to bind all modalities
Image Captioning
- Describe the content of an image or video with a natural language sentence
Encoder-decoder structure
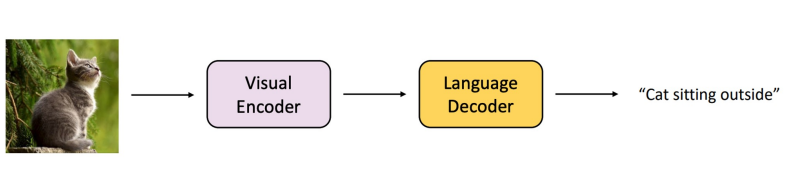
-
Visual Encoders
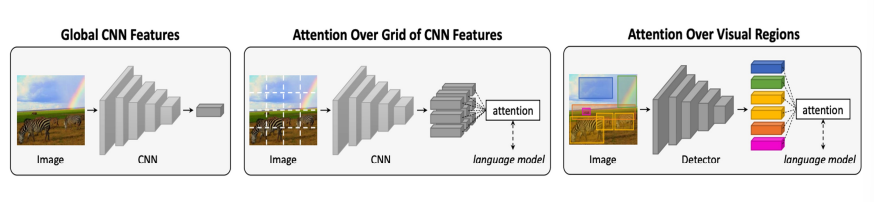
-
Visual Decoders

-
Show and Tell
- Encode the image with a CNN-based model
- Decode the image in an autoregressive fashion using an RNN (LSTM) language model

-
Bottom-up and Top-down attention
- Usually models operate on CNN features corresponding to a uniform grid
- What if we use features from object detections instead?

Video Captioning
- Video to text (sequence to sequence)
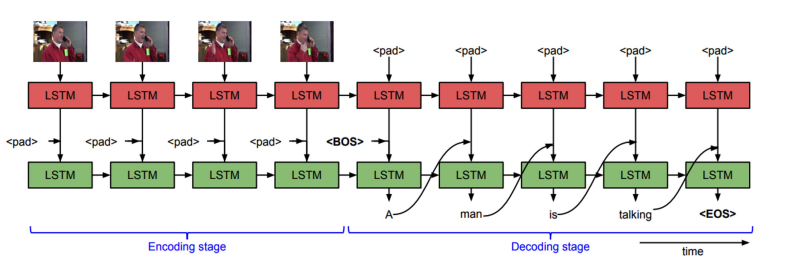
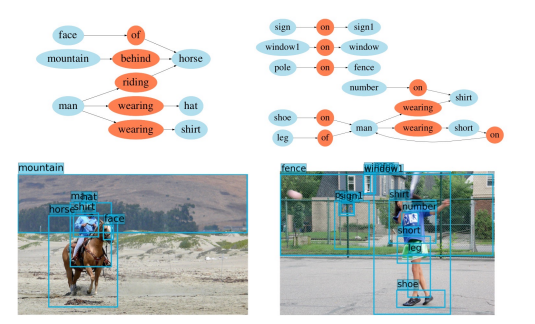
Scene graph
Scene graph is a structured way to represent information from images
Visual Question Answering
Answering open-ended questions about images which require an understanding of vision, language, and common sense knowledge
VQA as image + text → text

VQA as classification

Bottom-up and top-down attention

Visual Grounding
Locate relevant objects in the image
