Recurrent Neural Networks
So far: “Feedforward” Neural Networks
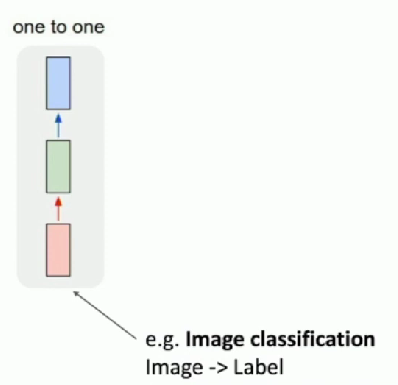
What about one to man?
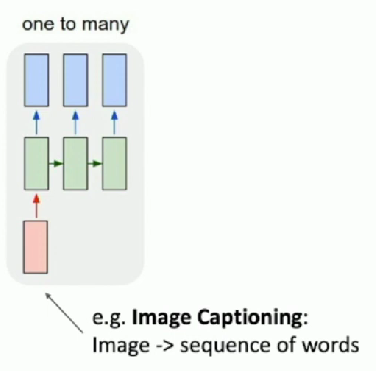
What about many to one?
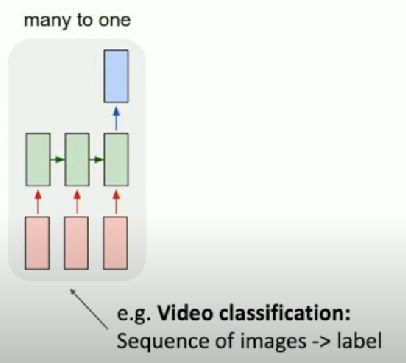
What about many to many?
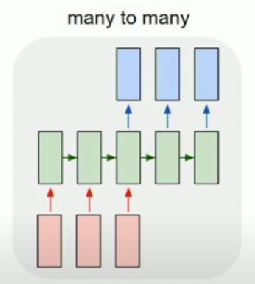
- Machine translation: sequence of words → sequence of words
Key Idea
We can process a sequence of vectors x by applying a recurrence formula at every time step:
Vanilla Recurrent Neural Networks
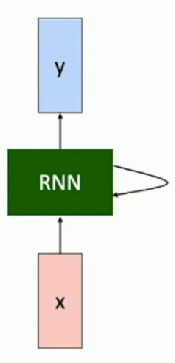
RNN Computational Graph
Initial hidden state
- Either set to all 0
- Or learn it
- Can only predict fixed input length
- depends on number of weight matrices
- Model size increase linearly with number of timesteps
- Different weights applied on different timesteps
- difficult to learn weights

Many to Many

Many to One

One to Many

Sequence to Sequence (Machine translation)
Many to One + One to Many
- Encoder + Decoder

Given characters 1, 2, …, t, model predicts character t
- Predicts at each time-step

At test-time, generate new text:
- sample characters one at a time
- feed back to model
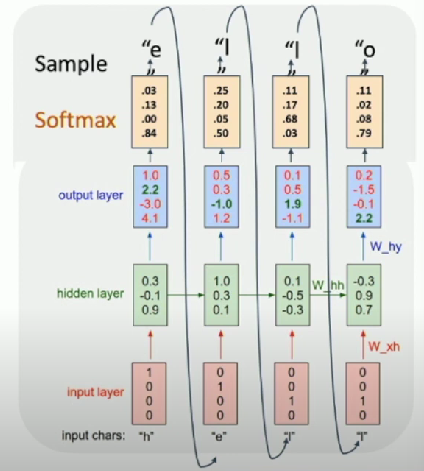

Matrix multiply with a one-hot-vector just extracts a column
- Often extract this into a separate embedding layer
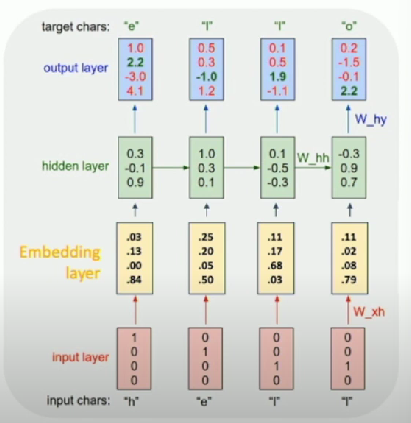
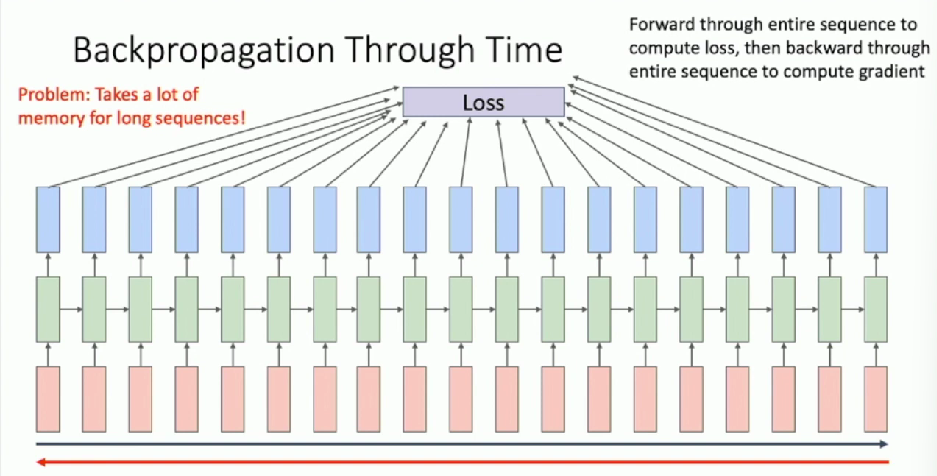
Backpropagation Through Time
Truncated Backpropagation Through Time
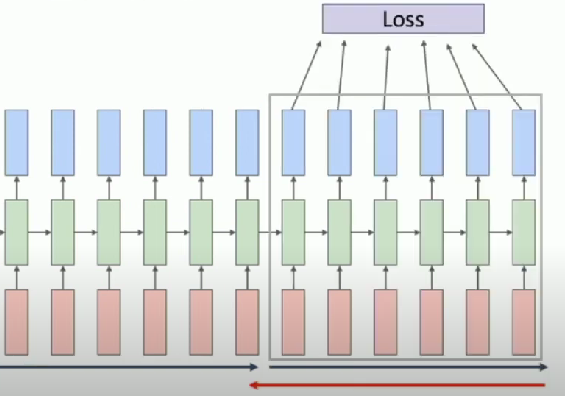
Run forward and backward through chunks of the sequence instead of whole sequence
Carry hidden states forward in time forever, but only backpropagate for some smaller number of steps
RNN Tradeoffs
Advantages
- Same weights applied on every timestep
- Can process any length input
- Computation for step t can use information from many steps back
- Model size doesn’t increase for longer input
Disadvantages - Recurrent computation is slow
- In practice, difficult to access information from many steps back
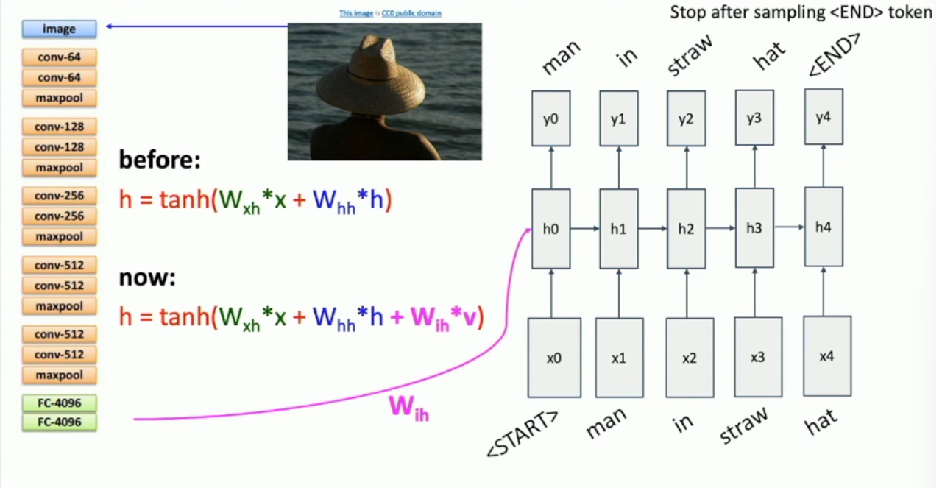
Example: Image Captioning
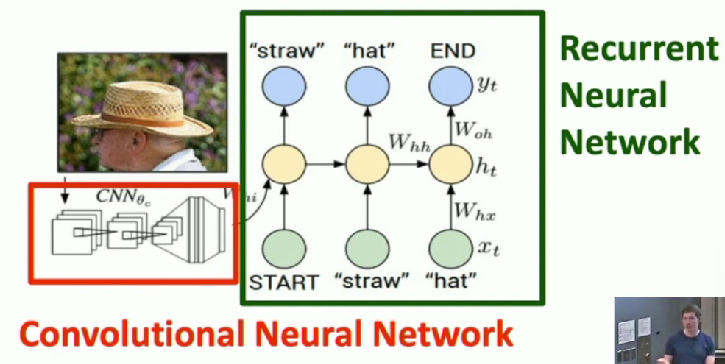
- Take feature vector coming out of CNN
- Feed into RNN

Result: