3D Shape Representations
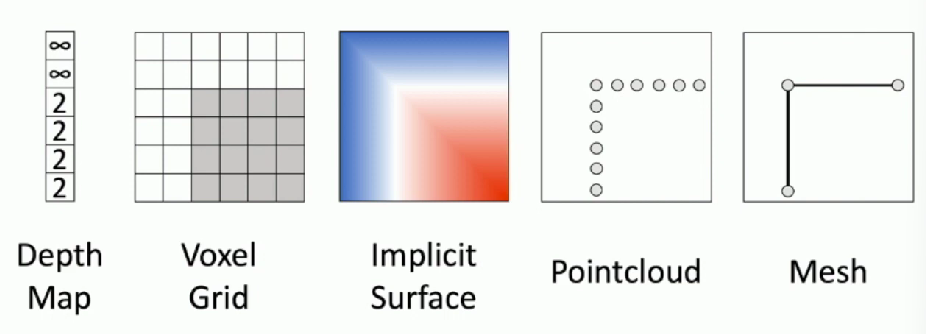
Depth Map
- RGB + Depth image = RGB-D Image (2.5D)
- This type of data can be recorded directly for some types of 3D sensors

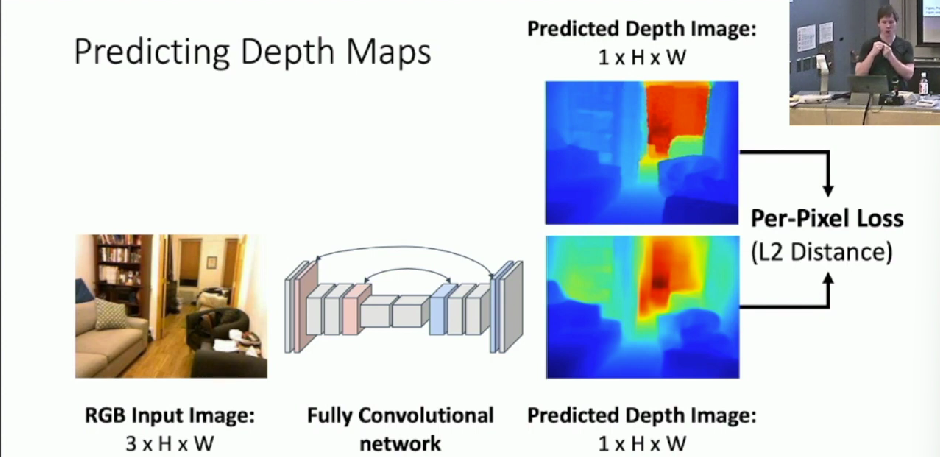
Predicting Depth Maps
Given an image, predict the depth map
We can use a fully convolutional network
A small, close object looks exactly the same as a larger, farther-away object
- Absolute scale / depth are ambiguous from a single image
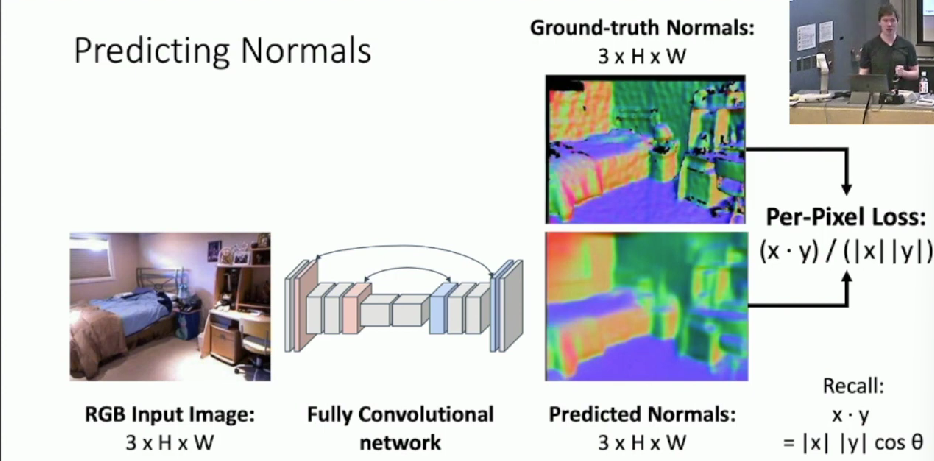
Surface Normals

Predicting Normals
Similar to depth maps
- Loss function is comparing angles between two vectors
Can predict depth map and normals with a single network
Voxel Grid
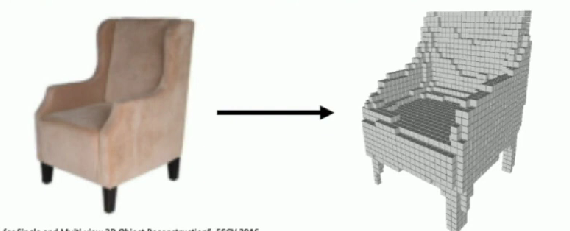
- Represent a shape with a V x V x V grid of occupancies
- Just like a segmentation masks in Instance Segmentation#Mask R-CNN, but in 3D
Scaling to high resolutions is nontrivial
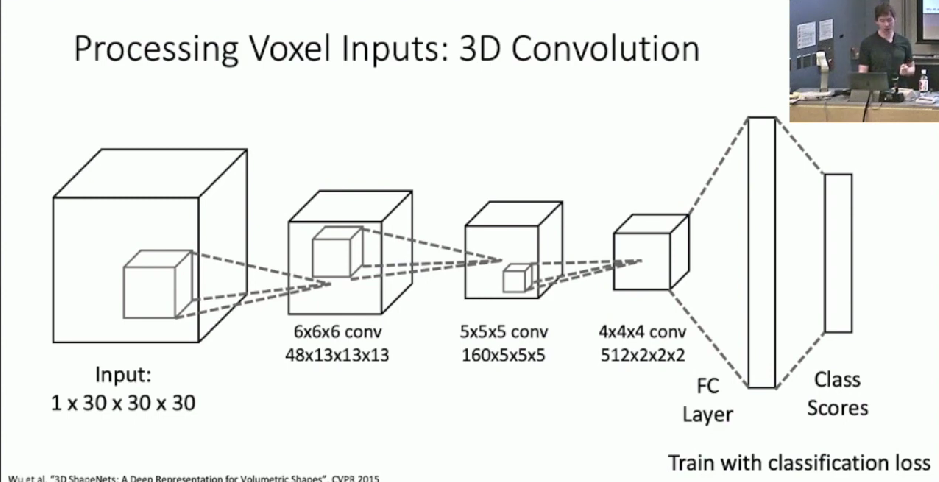
Processing Voxel Inputs: 3D Convolution
- Kernel is 3D cube sliding through input
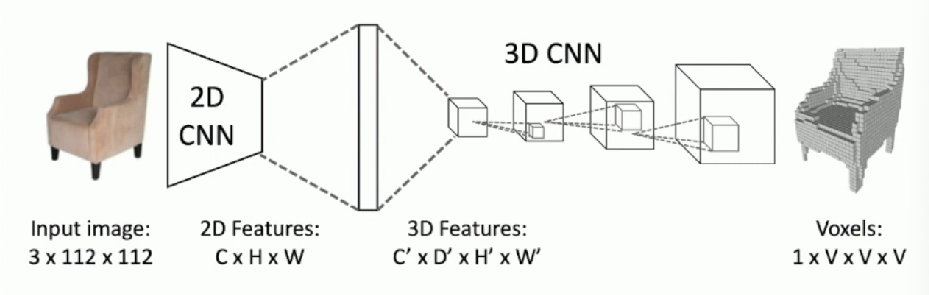
Generating Voxel Shapes: 3D Convolution
Voxel Problems: Memory Usage

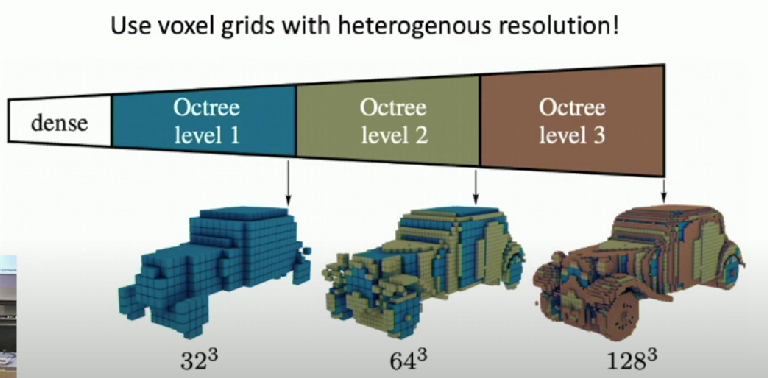
Scaling Voxels: Oct-Trees
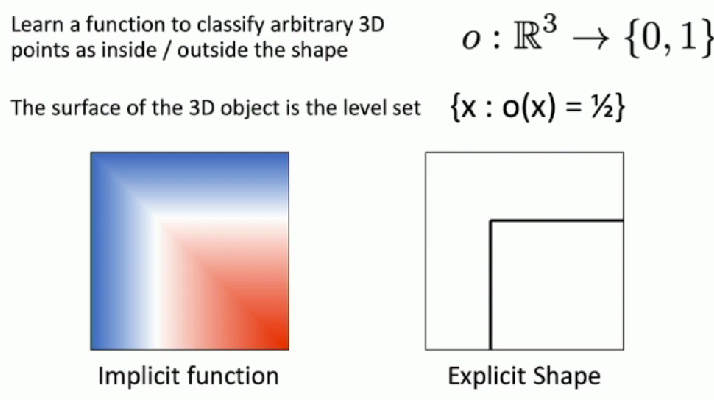
Implicit Functions
Learn a function to classify arbitrary 3D points as inside / outside the shape
The surface of the 3D object is the level set {x: o(x) = 1/2}
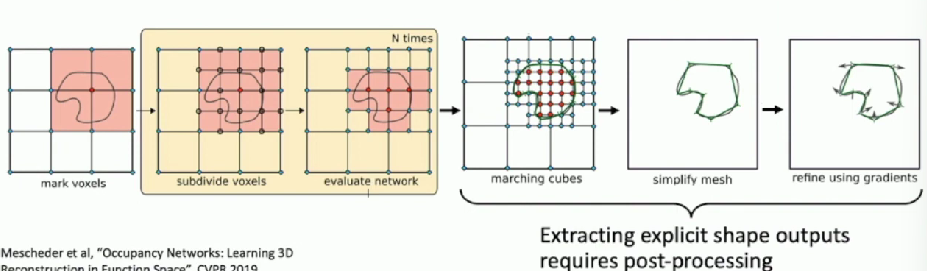
Point Cloud

- Represent shape as a set of P points in 3D space
- Requires new architecture, losses, etc
Extracting a mesh for rendering or other applications requires post-processing
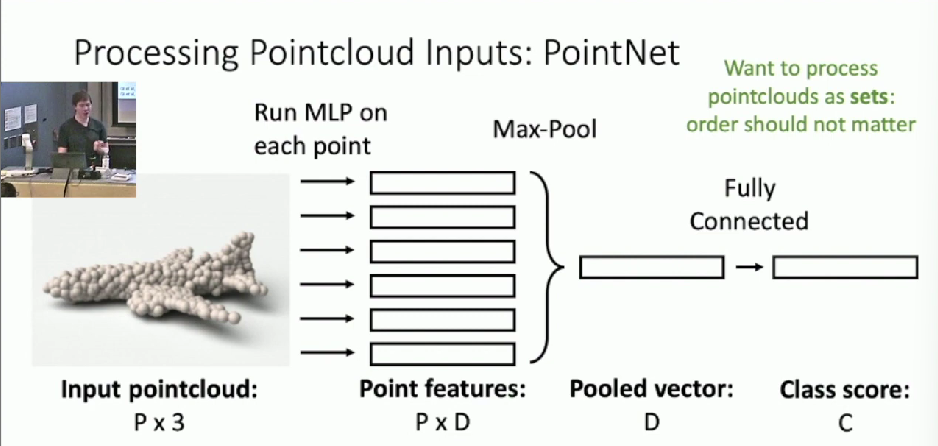
Processing Point Cloud Inputs: PointNet
Input: P points each with x, y, z positions
- Order of points should not matter
- Process pointclouds as set
Mesh
Triangle Mesh

Represent a 3D shape as a set of triangles
Vertices: Set of V points in 3D space
Faces: Set of triangles over the vertices
- Standard representation of graphics
- Explicitly represents 3D shapes
- Adaptive
- Can represent flat surfaces very efficiently
- Can allocate more faces to areas with fine details
- Can attach data on verts and interpolate over the whole surface
- RGB colors, texture coordinates, normal vectors, etc
Nontrivial to process with neural networks