Network Layer
Overview
- Transport segment from sending to receiving host
- On sending side, encapsulate segments in to datagrams
- On receiving side, delivers segments to transport layer
- Network layer protocols in every host, router
- Router examines header fields in all IP datagrams passing through it
Two Key Functions
Forwarding
- Move packets from router’s input to appropriate router output
Routing
- Determine route taken by packets from source to destination
Analogy: Taking a trip
Forwarding
- Process of getting through single interchange
Routing - Process of planning trip from source to destination
Data Plane
- Local, per-router function
- Determines how datagram arriving on router input port is forwarded to router output port
- Forwarding function
Control Plane
- Network-wide logic
- Determines how datagram is routed among routers along end-end path from source host to destination host
- Two Approaches:
- Traditional routing algorithms: implemented in routers
- Software-defined networking: implemented in servers
Router Architecture
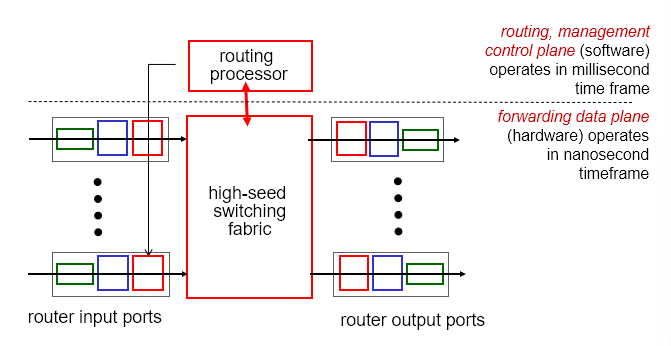
Input Port Functions
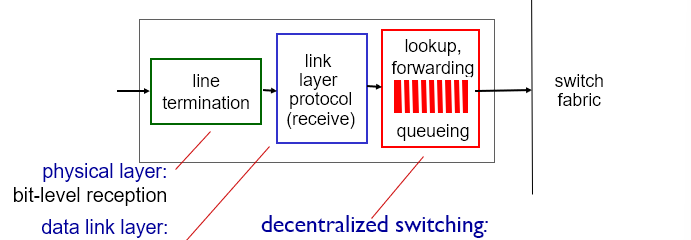
Decentralized Switching
- Using header field values, lookup output port using forwarding table in input port memory
- Goal: Complete input port processing at “line speed” (Max capacity)
- Queuing: if datagrams arrive faster than forwarding rate into switch fabric
Destination-based forwarding
Forward based only on destination IP address
Longest prefix matching
When looking for forwarding table entry for given destination address, use longest address prefix that matches destination address
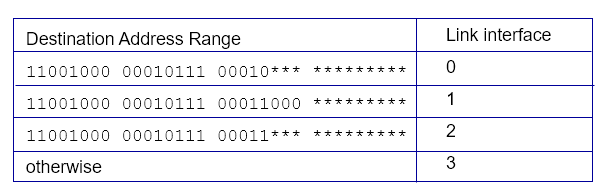
- Often performed using ternary content addressable memories (TCAMs)
- Content addressable: Present address to TCAM: retrieve address in one clock cycle, regardless of table size
Switching Fabrics
- Transfer packet from input buffer to appropriate output buffer
- Switching rate: Rate at which packets can be transferred from inputs to outputs
Three types:
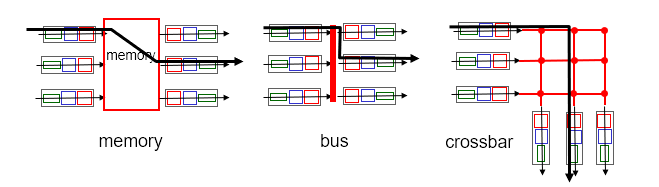
Switching via memory
First generation routers:
- Packet copied to system’s memory
- Limited by memory bandwidth
Switching via bus
- Datagram from input port memory to output port memory via a shared bus
- Bus contention: switching speed limited by bus bandwidth
Switching via interconnection network
- Overcome bus bandwidth limitations
- Fragmenting datagram into fixed length cells, switch cells through the fabric
Import port queuing
Fabric slower than input ports combined
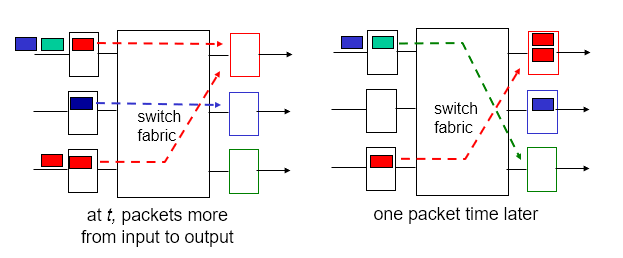
- Head of the Line Blocking
- Queued datagram at front of queue prevents others in queue from moving forward
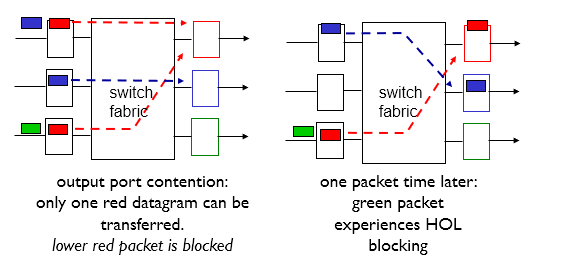
- Queued datagram at front of queue prevents others in queue from moving forward
Output port queuing
Buffering: Required when datagrams arrive from fabric faster than link transmission rate
Scheduling discipline: Chooses among queued datagrams for transmission
Packet Scheduling
Deciding which packet to send next on link
Internet Protocol (IP)
IPv4 and IPv6
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Generalized Forwarding
Control Plane
Routing: Determine route taken by packets from source to destination
- per-router control
- logically centralized control