Internet Protocol (IP)
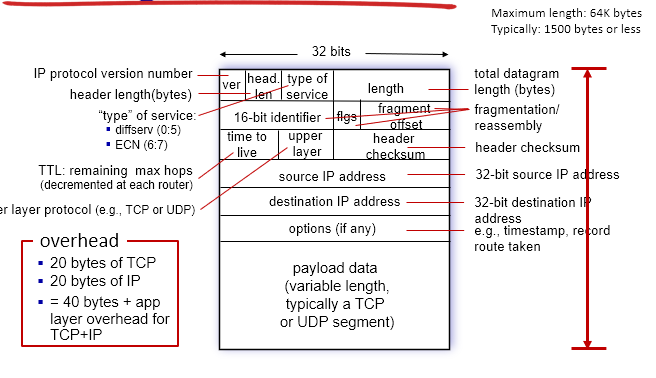
IP Datagram Format
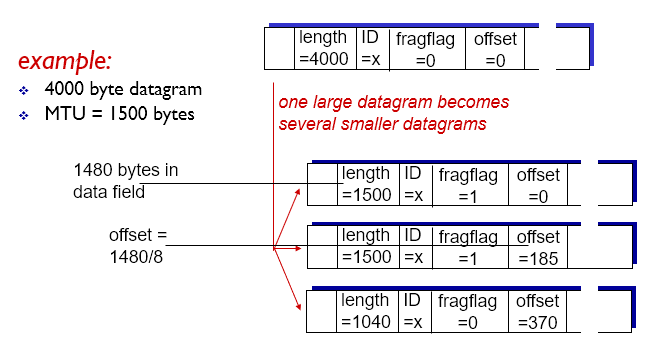
IP Fragmentation and Reassembly
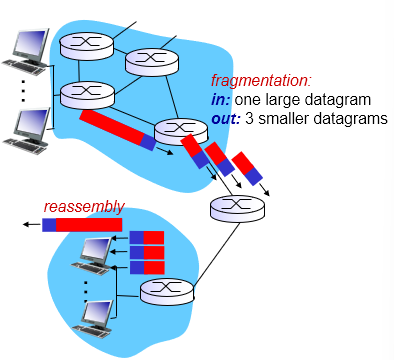
- Network links have MTU (Max transfer size)
- Largest possible link-level frame
- Large IP datagram divided within net
- Reassembled only at final destination
- IP header bits used to identify, order related fragments
IPv4 Addressing
IP address: 32-bit identifier for host, router interface
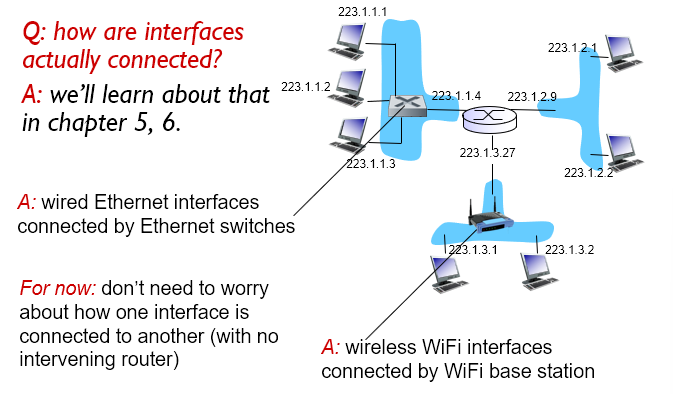
Interface: Connection between host/router and physical link
- Routers typically have multiple interfaces
- Host typically has one or two interfaces
IP address associated with each interface
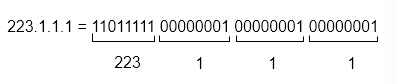
How are interfaces connected?
Subnets
Device interfaces with same subnet part of IP address
- Can physically reach each other without intervening router
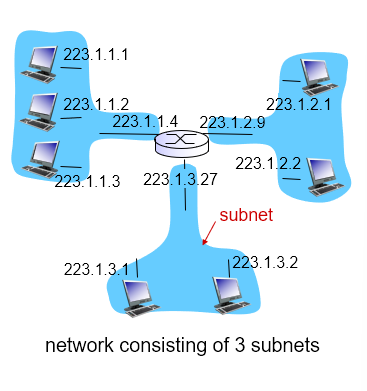
High order bits of IP address is subnet part, low order bits are host part
CIDR: Classless InterDomain Routing
- Subnet portion of address of arbitrary length
- Address format: a.b.c.d/x, where x is # bits in subnet portion of address

DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
How does a host get IP address
Dynamically get address from a server
Allow host to dynamically obtain its Ip address from network server when it joins network
- can renew its lease on address in use
- allow reus of addresses
- support for mobile users who want to join netowrk
Steps
- Host broadcasts DHCP discover msg (optional)
- DHCP server responds with DHCP offer msg (optional)
- Host requests IP address: DHCP request
- DHCP server sends address: DHCP ack

DHCP can return more than just allocated IP address on subnet:
- Address of first-hop router for client
- Name and IP address of DNS server
- Network mask
Hierarchical Addressing: route aggregation
Allows for efficient advertisement of routing information

IPv6
Motivation
32-bit address space soon to be completely allocated
Header format helps speed processing/forwarding
Header changes to faciliate QoS
Format
- Fixed-length 40 byte header
- No fragmentation allowed

Differences to IPv4
- Removed checksum
- Options: available as upper-layer, next-header protocol at router
- ICMPv6
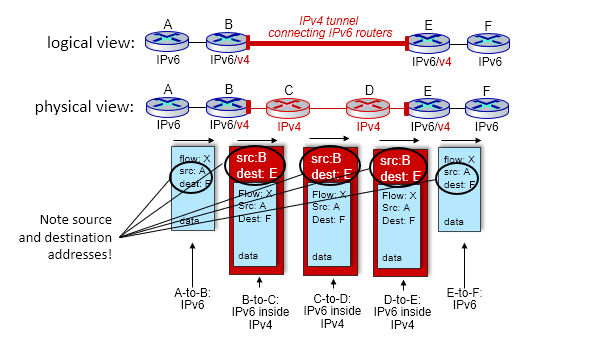
Transition from IPv4 to IPv6
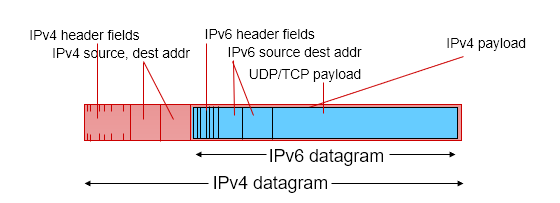
Tunneling: IPv6 datagram carried as payload in IPv4 datagram among IPv4 routers